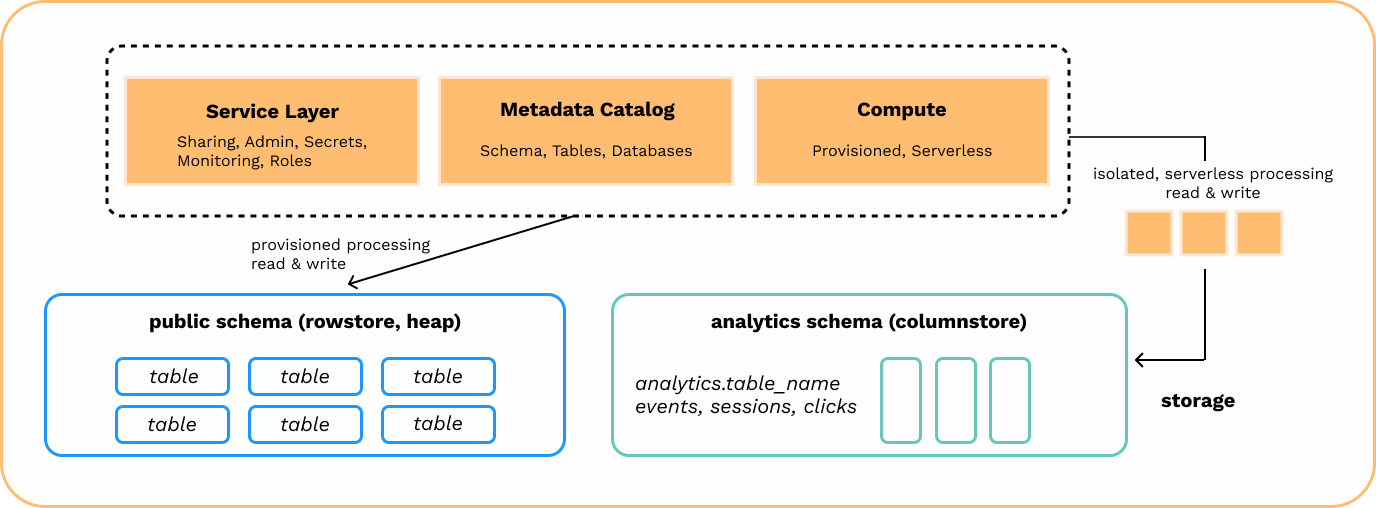
 Hydra adds serverless online analytics processing (OLAP) functionality to Postgres. Hydra is column-oriented by default: to enable serverless analytics, simply create a table.
Hydra makes it easier to build realtime analytics by automatically managing the transactional rowstore and analytical columnstore together. Inserting data into a table will automatically convert it into an optimized columnar format.
Hydra runs isolated resources (CPU & RAM) per process, removing the potential for resource contention with Postgres’ transactional rowstore. Data in analytics tables benefit from efficient compression of 5-15X and is ideal for large data volumes. For example: 150GB compresses to 15GB with a 10X compression rate.
Hydra adds serverless online analytics processing (OLAP) functionality to Postgres. Hydra is column-oriented by default: to enable serverless analytics, simply create a table.
Hydra makes it easier to build realtime analytics by automatically managing the transactional rowstore and analytical columnstore together. Inserting data into a table will automatically convert it into an optimized columnar format.
Hydra runs isolated resources (CPU & RAM) per process, removing the potential for resource contention with Postgres’ transactional rowstore. Data in analytics tables benefit from efficient compression of 5-15X and is ideal for large data volumes. For example: 150GB compresses to 15GB with a 10X compression rate.
Postgres as a multi-workload data store
Hydra is a “multi-workload data store” with the following core capabilities:- high throughput, ACID-compliant online transactional processing (OLTP)
- vectorized, parallel execution of online analytical processing (OLAP)
What's a rowstore?
What's a rowstore?
In a rowstore, table rows are stored sequentially. This arrangement enables fast retrieval of rows because the column values for each row are grouped together. A rowstore make it easy to add / modify a record, but may scan unnecessary data during read operations. For example, PostgreSQL is a rowstore..png)
.png)
What's a columnstore?
What's a columnstore?
In a columnstore, tables are organized by storing all the values of each column in sequence. This format enhances the efficiency of filtering or aggregating columns but complicates the retrieval of individual rows due to the gaps between row data. For example, DuckDB is a columnstore..png)
.png)
Analytics overview
- Isolated Compute Tenancy
- Serverless processing
- Sharing
